Which Is an Example of Base Rate Fallacy
So set the True state variable for Woman has cancer 001. Over half of car accidents occur within five miles of home according to a report by Progressive Insurance in 2002.

Failure To Account For Base Rate How It Affects Your Decision Making Process Welcome To Club Street Post
An example of the base rate fallacy is the false positive paradox.

. This paradox describes situations where there are more false positive test results than true positives. An example of the base rate fallacy is the false positive paradox. The base rate fallacy is a logical fallacy that occurs when someone evaluates the probability of an event by using the base rate instead of considering other relevant information.
- There is a 12 chance 15. For example consider a specific disease that occurs in 11000 patients tested. The base rate fallacy also called base rate neglect or base rate bias.
Answer to Exercise 6. When something says 50 extra free only a third 33 of what youre looking at is free. In this example we have 100 individuals 80 of whom are vaccinated and 20 of whom are unvaccinated.
Base Rate Fallacy Defined. 11 First participants are given the following base rate information. Statistically speaking your child may still have a.
There are two cab companies in a city. Probability neglect a term coined by Sunstein 2002. Example 1 - The cab problem.
Thinking that this means vaccines are ineffective is an example of a base rate fallacy or. The base rate fallacy is based on a statistical concept called the base rate. According to market efficiency new information should rapidly be assimilated and reflected instantly in a securitys price.
This paradox describes situations where there are more false positive test results than true positives. Jeremy believes all people from the Middle-East are terrorists. Another random variable represents the positive test result from the mammogram test.
Lots of food companies exploit the Base Rate Fallacy on their packaging. Understanding the base rate fallacy. This is an example of Base Rate Fallacy because the subjects neglected the initial base rate presented in the problem 85 of the cabs are green and 15 are blue.
Unbiased empirical tests demonstrate that a small but noticeable. The base rate fallacy is committed when a person focuses on specific information and ignores generic information relating to the overall likelihood of a given event. The Base rate fallacy is a common cognitive error that skews decision-making whereby information about the occurrence of some common characteristic within a given population is ignored or not given.
You may recall having heard this statistic before or. Neglecting base rates base rate neglect prosecutors fallacy form of. In simple terms it refers to the percentage of a population that has a specific characteristic.
Cherri assumes all accountants dress in suits and ties. The base rate of global. One is the Green company the other is the Blue company.
Which is an example of base rate fallacy. CORRECT Mary knows one person from Meridian high Who is boring so she thinks everyone from that school is boring. The base rate of office buildings in New York City with at least 27 floors is 1 in 20 5.
To find the base percentage and rateperce ntage base rate rate in decimalbase percentagerate rate in decimalrate percentagebase 100ExampleBase 10Percentage 2RateRate 210. 3 rows The base rate fallacy is a tendency to focus on specific information over general probabilities. For example if a facial recognition camera can identify wanted criminals 99 accurately but analyzes 10000 people a day the high accuracy is outweighed by the number of.
The False state probability will be calculated automatically as 1 -. We have a base rate information that 1 of the woman has cancer. A simple example of this would involve the diagnosis of a condition in a patient.
Using this information to claim vaccines are ineffective is an example of a base rate fallacy or base rate bias. According to market efficiency new. For example if a facial recognition camera can identify wanted criminals 99 accurately but.
Matthew thinks all women are crazy. With strong ties to the concept of base rate fallacy overreaction to a market event is one such example. The base-rate fallacy is fed by other biases for instance uniqueness bias which results in extreme base-rate neglect because the case at.
In settings where the majority of people are vaccinated it may be true that there is an equal number of people or even a greater number of people who are vaccinated and become infected. However the base rate fallacy offers an explanation as to why investors overreact to a market event. For example if you are told that 90 of people who have cancer will die from it and then asked to evaluate what percentage of people with cancer will die from it most people would say 90 because they.
Faith healing works but not all the time especially when ones faith is not strong enough as generally indicated by the size of ones financial offering. 6263 to denote the situation where people overfocus on bad outcomes with small likelihoods for instance terrorist attacks is a special case of the base-rate fallacy. Base Rate Neglect Example.
The tendency to ignore or underuse base rate information and instead to be influenced by the distinctive features of the case being judged is known as base rate fallacy. This classic example of the base rate fallacy is presented in Bar-Hillels foundational paper on the topic. The problem should have been solved as follows.
This means it may be true that there is an equal or even greater number of people who are vaccinated and become infected.

What Is Base Rate Fallacy And Why It Matters In Business Fourweekmba
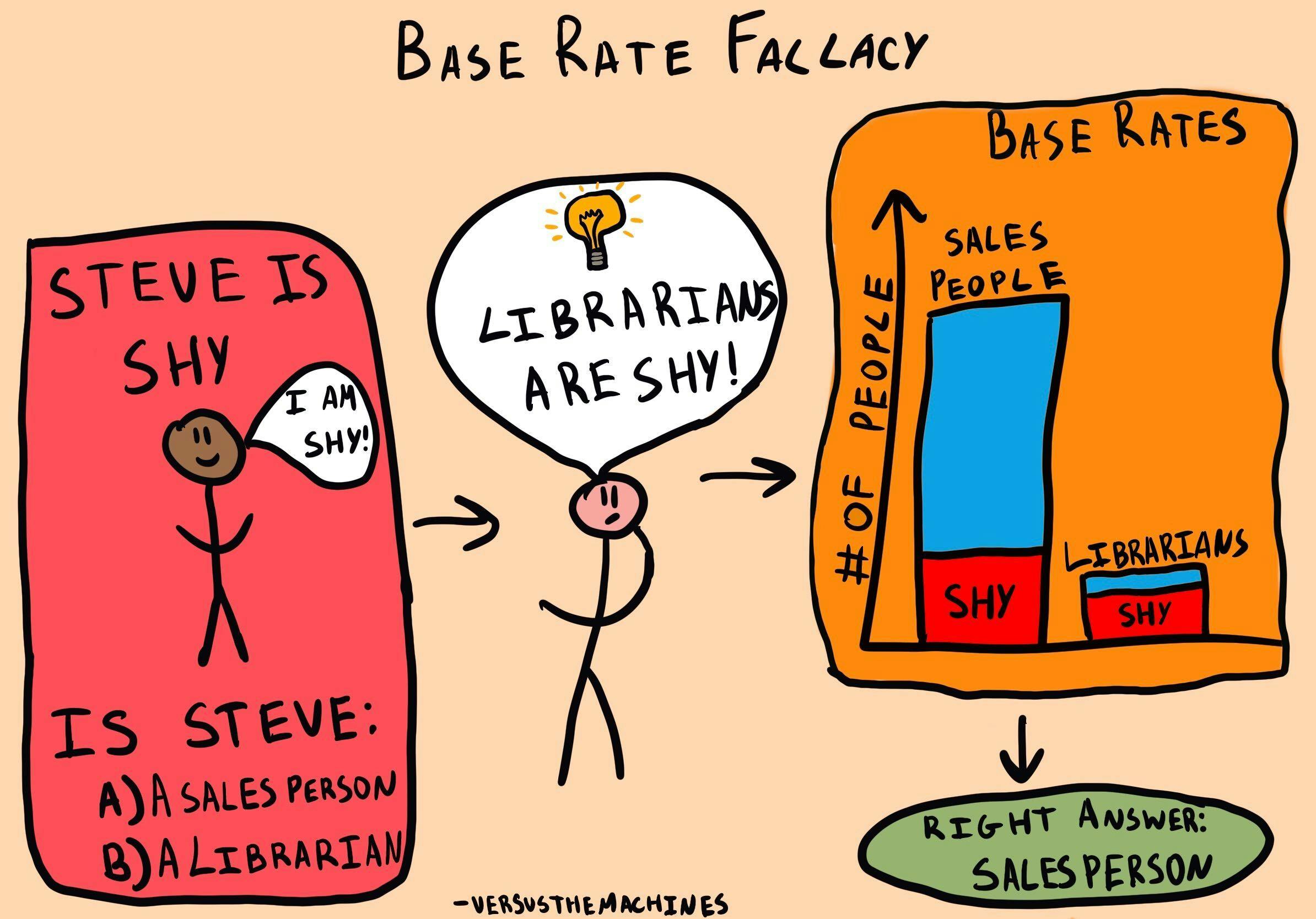
Base Rate Fallacy The Decision Lab

Why We Keep Misunderstanding The Covid 19 Numbers The Base Rate Fallacy The Good Information Project

No comments for "Which Is an Example of Base Rate Fallacy"
Post a Comment